Your joints are the foundation of your mobility, allowing you to stay active and pain-free. But did you know your body can’t produce one of the most important nutrients for joint health, omega-3 fatty acids? These essential fats must come from your diet or supplements, making them a critical part of keeping your joints in top shape.
Omega-3s are more than just helpful, they’re vital. They reduce inflammation, protect cartilage from wear and tear, and improve joint lubrication, ensuring smoother movement.
In this guide, we’ll dive into why omega-3s are non-negotiable for healthy joints, how they work, and practical ways to add them to your routine. Let’s explore how this essential nutrient can keep you moving with ease.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that your body cannot produce on its own, meaning you need to get them from food or supplements. They are well-known for their role in supporting heart and brain health, but they’re equally vital for joint health.
Types of Omega-3s
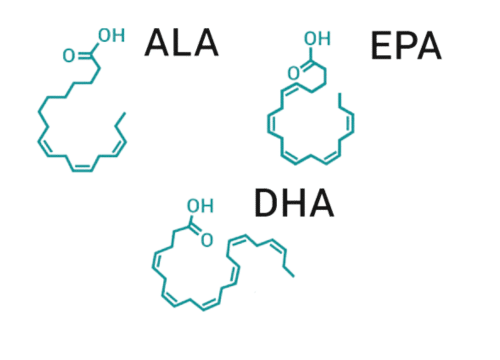
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids, each with unique benefits:
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid):
ALA, the most common omega-3 in the human diet, is found in plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. While it offers some health benefits, your body needs to convert ALA into EPA and DHA to unlock its full anti-inflammatory potential. Unfortunately, this conversion is minimal, making marine-based sources a more effective option for meeting your omega-3 needs.
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid):
EPA, found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, is a key nutrient for combating inflammation. It supports your joints by producing eicosanoids compounds that regulate inflammatory responses and protect against damage. This makes EPA especially valuable for managing arthritis and joint pain, helping to ease discomfort and promote better mobility.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid):
DHA, another essential marine-based omega-3, plays a vital role in maintaining overall cellular health by strengthening cell membranes. In joints, it helps preserve cartilage integrity and ensures smooth communication between cells, which is critical for tissue repair and maintenance. Its anti-inflammatory properties work hand-in-hand with EPA, providing comprehensive support to reduce joint discomfort and promote long-term joint health.
Why Omega-3s Matter for Joint Health
Reducing Inflammation and Supporting Joint Function
Chronic inflammation is a major cause of joint pain and stiffness, especially in conditions like arthritis. Omega-3s work by blocking the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines and prostaglandins, that cause swelling and discomfort. At the same time, they enhance anti-inflammatory responses, creating a balance that helps reduce pain and improve joint function. Think of omega-3s as your body’s internal cool-down mechanism, soothing inflammation and supporting smoother, more comfortable movement.
Protecting Cartilage and Preventing Degeneration
Cartilage is the soft, flexible tissue that cushions your joints, but it can wear down over time due to inflammation or aging. Omega-3s help protect cartilage by reducing enzymes that break it down and promoting the production of new cartilage cells. By maintaining healthy cartilage, omega-3s reduce joint stiffness and slow the progression of degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis. It’s like providing your joints with a long-lasting cushion, protecting them from daily wear and tear.
Enhancing Quality of Life for Joint-Related Conditions
For those living with joint-related conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, omega-3s offer much-needed relief. Studies show that omega-3s can reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups, improving joint flexibility and reducing swelling. Whether it’s easing morning stiffness or making daily tasks less painful, omega-3s help enhance your quality of life by keeping your joints more functional and less painful.
Supporting Bone Health
Healthy bones are just as important as healthy cartilage for joint function. Omega-3s improve calcium absorption and reduce bone loss, making your bones stronger and better able to support your joints. This is especially important as you age when the risk of osteoporosis and joint-related bone issues increases. By strengthening your bones, omega-3s ensure your joints stay stable and durable.
Improving Synovial Fluid Function
Synovial fluid is the lubricant that keeps your joints moving smoothly and painlessly. Omega-3s enhance the quality of this fluid, reducing friction between bones and easing stiffness, especially in the mornings or after long periods of inactivity. With better joint lubrication, movements feel more effortless, allowing you to stay active and mobile.
Enhancing Blood Flow to Joints
Good circulation is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to your joints, supporting repair, and reducing inflammation. Omega-3s improve blood flow, ensuring that your joints get the nutrients they need to stay healthy and heal from daily wear. Better circulation also helps flush out waste products from inflamed areas, promoting faster recovery and relief from stiffness
From reducing inflammation to improving joint lubrication, omega-3s offer a comprehensive solution for joint health. But how can you ensure you’re getting enough of these powerful nutrients? Let’s explore the best sources of omega-3s and how to incorporate them into your daily routine for maximum benefits.
Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are vital for joint health, and the good news is that there are plenty of ways to get them. Whether you prefer fish, plant-based options, or supplements, there’s a source that fits your lifestyle. Here’s a breakdown of the best options to help you meet your omega-3 needs.
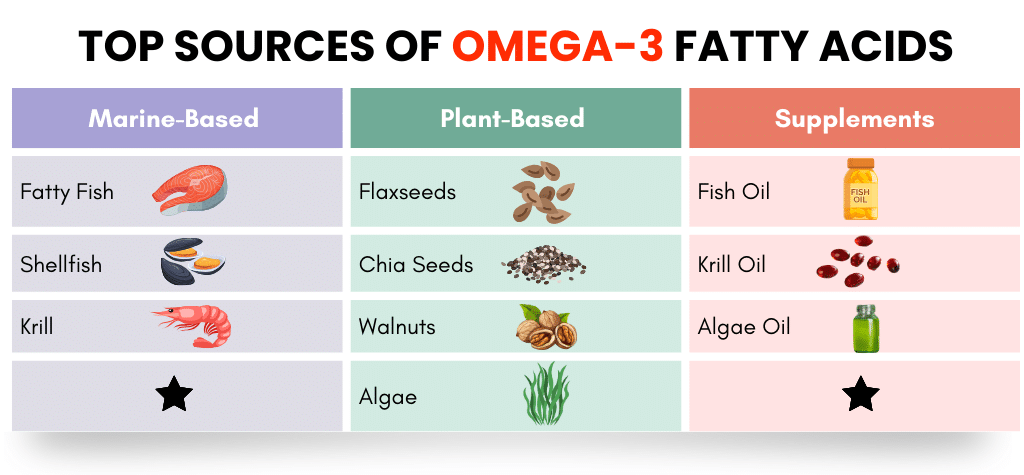
Marine-Based Sources
1. Fatty Fish
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are among the richest natural sources of omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA. These omega-3s are directly linked to reducing inflammation and supporting joint health. A serving of salmon, for example, can provide over 1,000 mg of combined EPA and DHA, making it a convenient and delicious choice. Grill it, bake it, or add it to salads for an easy omega-3 boost.
2. Shellfish
Shellfish like oysters and mussels also contain omega-3s, though in smaller amounts compared to fatty fish. They’re a great alternative for those looking to diversify their seafood options. Plus, shellfish come with the added benefit of being high in zinc, which supports overall joint and bone health.
3. Krill
Krill is a tiny crustacean found in cold ocean waters that is the most bioavailable sources of omega-3s. Unlike fish oil, the omega-3s in krill oil are bound to Phospholipids, making them easier for your body to absorb. As a bonus, krill oil contains astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant that supports skin and joint health.
Plant-Based Sources
1. Flaxseeds
Flaxseeds are one of the best plant-based sources of ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), an omega-3 your body can partially convert into EPA and DHA. Sprinkle ground flaxseeds on oatmeal, yogurt, or smoothies for an easy and nutritious addition to your meals.
2. Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are another excellent source of ALA, providing a good amount of omega-3s along with fiber and protein. They’re incredibly versatile. Add them to puddings, salads, or baked goods for a simple way to boost your intake.
3. Walnuts
Walnuts are not only a convenient snack but also a good source of ALA. Just a handful of walnuts can contribute to your daily omega-3 needs while providing other nutrients like magnesium and antioxidants that support joint health.
4. Algae
For those following a plant-based diet, algae oil is a standout option. Unlike other plant-based sources, algae oil contains DHA and EPA, the same omega-3s found in fish. It’s an excellent alternative for vegetarians and vegans who want the benefits of marine-based omega-3s without eating seafood.
Supplements
1. Fish Oil
Fish oil supplements are one of the most popular ways to get omega-3s. They provide high doses of EPA and DHA, making them a reliable choice for those who don’t eat enough fish. When choosing a fish oil supplement, look for options that are purified and tested for contaminants like mercury.
2. Krill Oil
Krill oil supplements offer many of the same benefits as fish oil but with better absorption and the added benefit of Astaxanthin. They’re a great choice for those looking for a premium omega-3 option with antioxidant protection.
3. Algae Oil
Algae oil supplements are ideal for vegans and vegetarians. They’re rich in DHA and often EPA, making them one of the best plant-based alternatives to fish oil.
Tips for Getting the Most Out of Omega-3s
- Incorporate Fatty Fish into Meals: Aim for at least two servings of fatty fish per week for optimal EPA and DHA intake.
- Mix in Plant-Based Options: Add chia seeds, flaxseeds, or walnuts to your daily meals for an easy omega-3 boost.
- Consider Supplements: If dietary sources aren’t enough, choose a high-quality omega-3 supplement that fits your needs.
Now that you know where to find omega-3s, here’s the good part: it’s easier than you think to incorporate these sources into your daily routine. Up next, let’s explore how much omega-3 you need and the best ways to meet your goals for joint health.
How Much Omega-3 Do You Need for Joint Health?
Getting the right amount of omega-3 fatty acids can make a big difference in keeping your joints healthy. While the exact amount you need may depend on your lifestyle and health conditions, here are some general guidelines to help you hit the sweet spot for joint support.
General Recommendations
For joint health, experts typically recommend a daily intake of 250-500 mg of combined EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). These two marine-based omega-3s are the ones that actively reduce inflammation and promote joint comfort. If you’re dealing with arthritis or chronic joint pain, studies suggest that higher doses up to 1,000-3,000 mg of EPA and DHA daily may offer greater relief.
How to Meet Your Omega-3 Needs
1. Through Diet
Two servings of fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, or sardines, per week can help you meet the recommended omega-3 levels. A single serving of salmon, for example, provides around 1,500-2,000 mg of EPA and DHA. Pair it with plant-based sources like flaxseeds or walnuts to round out your intake.
2. Through Supplements
If eating fish regularly isn’t practical, omega-3 supplements are an easy alternative. Fish oil and krill oil supplements provide concentrated doses of EPA and DHA, making it simple to hit your daily targets. For vegetarians or vegans, algae oil is an excellent source of DHA and sometimes EPA. Always check the label to ensure you’re getting at least 250-500 mg per serving of combined EPA and DHA.
What If You Need More?
People with arthritis, joint injuries, or high levels of inflammation may benefit from higher omega-3 doses. In these cases, supplements are often the best option because they provide consistent, higher concentrations of EPA and DHA. However, it’s always a good idea to consult a healthcare provider before exceeding 3,000 mg per day, as very high doses may increase the risk of bleeding.
Tips for Consistency
- Start Small: If you’re new to omega-3s, begin with the lower end of the recommended range and gradually increase based on your needs.
- Make It Routine: Take supplements at the same time each day, such as during breakfast, to make it a habit.
- Combine with Food: Omega-3s are better absorbed when taken with meals that include healthy fats, like avocados or nuts.
Now here comes the good part: with the right omega-3 intake, you’re giving your joints the tools they need to stay flexible, pain-free, and strong. But how can you ensure your omega-3 sources are working effectively? Let’s look at potential side effects and tips to maximize the benefits safely.
Are Omega-3 Supplements Better Than Food Sources?
Both omega-3 supplements and food sources have their advantages. Food sources like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts provide additional nutrients alongside omega-3s, making them a natural and nutrient-rich choice. However, supplements offer a concentrated and convenient way to meet your daily omega-3 needs, especially if you don’t consume enough omega-3-rich foods regularly.
For optimal results, a combination of both is often the best approach. Incorporate omega-3-rich foods into your diet and use supplements to fill any gaps. Always choose high-quality supplements to ensure purity and effectiveness.
Potential Side Effects for Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids are generally safe for most people, but like any supplement or dietary change, there are a few things to keep in mind. Understanding potential side effects and how to avoid them ensures you can enjoy all the benefits without any unnecessary discomfort.
1. Digestive Issues
Some people may experience mild stomach discomfort, including nausea, bloating, or diarrhea, especially when first starting omega-3 supplements. These effects are often temporary and can be minimized by taking supplements with meals or splitting the dose throughout the day.
2. Fishy Aftertaste or Burps
Fish oil supplements, in particular, can leave a lingering fishy aftertaste or cause “fish burps.” Choosing enteric-coated capsules or freezing the supplements before taking them can help reduce this issue. Krill oil and algae oil tend to have a milder taste and are less likely to cause this problem.
3. Blood Thinning
Omega-3s can thin the blood slightly, which is beneficial for heart health but may increase the risk of bleeding, especially for those on blood-thinning medications like aspirin or warfarin. If you bruise easily or have a surgery planned, consult your doctor before taking high doses.
4. Allergic Reactions
People with seafood allergies should be cautious with fish oil or krill oil supplements. Algae oil is a safe alternative for vegetarians, vegans, or those with allergies.
How to Safely Maximize Omega-3 Benefits
1. Choose High-Quality Supplements
Not all omega-3 supplements are created equal. Look for products that are third-party tested for purity and potency, ensuring they’re free from contaminants like mercury and heavy metals. Sustainable sourcing, particularly for krill oil, is another factor to consider.
2. Pair Omega-3s with a Healthy Lifestyle
Omega-3s are most effective when combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise. Anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, berries, and nuts complement omega-3s, enhancing their benefits for joint health.
3. Take It Consistently
Whether you’re getting omega-3s from food or supplements, consistency is key. Incorporating them into your daily routine ensures your joints receive regular support to stay healthy and pain-free.
Conclusion
Your joints work hard every day, supporting every step, stretch, and stride. Keeping them healthy doesn’t have to be complicated. Omega-3 fatty acids are a simple yet powerful way to protect your joints from inflammation, stiffness, and long-term wear.
Whether you’re eating a serving of salmon, sprinkling chia seeds into your smoothie, or taking a quality supplement, omega-3s provide the tools your joints need to stay flexible and resilient. These essential fats aren’t just for easing pain, they’re for preserving the freedom to move comfortably at every stage of life.
Don’t wait for joint discomfort to slow you down. Start incorporating omega-3s into your daily routine now, and let them support you in staying active and pain-free for years to come.