For years, fish oil has been a top choice for managing cholesterol and supporting heart health. But recently, krill oil has emerged as a rising star, praised for its superior absorption, unique antioxidant properties, and eco-friendly appeal. This has sparked an important question: which one is the better option?
Fish oil is celebrated for its high omega-3 content and affordability, making it a reliable staple for many. Krill oil, on the other hand, offers distinct advantages like phospholipid-bound omega-3s for faster absorption and astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant. While both bring significant health benefits, the right choice depends on your priorities and health goals.
In this guide, we’ll dive into the unique features of krill oil and fish oil, their impact on cholesterol, and how to decide which is best for you. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which supplement deserves a place in your routine. Read on to make an informed decision for your heart health!
Overview of Krill Oil and Fish Oil
Krill oil and fish oil are two popular omega-3 supplements, but they come from different sources and have unique characteristics. Krill oil is extracted from krill, tiny crustaceans found in cold ocean waters. It contains omega-3 fatty acids (DHA and EPA) bound to phospholipids, which makes it easier for your body to absorb. It also includes astaxanthin, a natural antioxidant that keeps the oil stable and adds protective benefits.
Fish oil, on the other hand, comes from fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. Its omega-3s are in triglyceride form, which requires more processing in the body for absorption. Although it lacks natural antioxidants like astaxanthin, fish oil is widely studied and has long been a trusted source of omega-3s.
How Krill Oil and Fish Oil Affect Cholesterol Levels
Krill Oil’s Impact on Cholesterol
Krill oil excels at improving cholesterol levels. Research shows it can lower LDL (bad cholesterol) while increasing HDL (good cholesterol), making it a great option for heart health. Its omega-3s are bound to phospholipids, which are easily absorbed into your cell membranes. This enhanced absorption makes krill oil particularly effective in reducing cholesterol and inflammation.
Additionally, krill oil has been shown to lower triglycerides, another type of fat in your blood that increases the risk of heart disease. Its secret weapon is astaxanthin, a natural antioxidant that fights oxidative stress—a key factor in cholesterol buildup and arterial damage.
Fish Oil’s Impact on Cholesterol
Fish oil is well-known for its ability to lower triglycerides, making it a popular choice for supporting heart health. However, its impact on LDL and HDL cholesterol is less predictable. Some studies suggest minor improvements, while others indicate little to no effect on these markers.
The real strength of fish oil lies in its ability to reduce inflammation. By decreasing inflammation, fish oil indirectly supports better cholesterol management and overall cardiovascular health. However, it doesn’t contain the phospholipids or natural antioxidants found in krill oil, which means it may not offer as many comprehensive benefits.
Krill Oil vs. Fish Oil: Which Wins the Cholesterol Battle?
When it comes to managing cholesterol and supporting heart health, krill oil and fish oil are both strong contenders. They’re loaded with omega-3 fatty acids that your heart loves, but which one deserves a permanent spot in your routine? Let’s compare the key factors that set them apart.
Bioavailability
Bioavailability is about how easily your body can absorb and use the nutrients in a supplement. Krill oil contains omega-3s bound to phospholipids, a structure that allows the fatty acids to blend seamlessly into your cell membranes. This means your body gets more bang for its buck with less effort.
Fish oil, on the other hand, has omega-3s in triglyceride form, which requires extra processing in your digestive system. While still effective, it may take longer for your body to break down and use these nutrients, especially if your digestion isn’t running at full speed.
Winner: Krill oil, for its fast absorption and efficiency.
Antioxidants
Krill oil has a built-in bonus: astaxanthin, a natural antioxidant that gives it a reddish color and protects the oil from going bad. This isn’t just good for shelf life—it also provides extra protection for your cells by reducing oxidative stress.
Fish oil lacks this natural protection and is more prone to oxidation, which can cause it to spoil faster. Oxidized oils can lose their health benefits and may even have a negative impact on your body. While some fish oil brands add antioxidants like vitamin E to extend shelf life, it’s not the same as having a natural antioxidant like astaxanthin built right in.
Winner: Krill oil, thanks to its powerful natural antioxidant.
Sustainability
The environmental impact of your supplements is something to think about. Krill is one of the most abundant species on Earth, and its harvesting is typically well-regulated to avoid overfishing. Responsible krill fisheries also ensure minimal disruption to marine ecosystems, keeping the food chain intact for other species.
Fish oil, however, is often sourced from species like anchovies or mackerel, which are more vulnerable to overfishing. Unsustainable practices can harm marine biodiversity and even contribute to the depletion of certain fish populations.
Winner: Krill oil, for its more eco-conscious harvesting practices.
Taste and Digestibility
If you’ve ever experienced “fish burps” after taking fish oil, you know the struggle is real. The oil’s tendency to repeat on you isn’t just unpleasant—it’s also a sign that your stomach may not be digesting it efficiently.
Krill oil is much gentler on your stomach and less likely to cause that fishy aftertaste. Its phospholipid structure again plays a role here, making it easier for your digestive system to handle. For anyone with a sensitive stomach, krill oil feels like the more comfortable choice.
Winner: Krill oil, for its smoother digestion and lack of fishy burps.
Price
Here’s where fish oil has the upper hand. Fish oil supplements are widely available and generally more affordable. If you’re on a tight budget, fish oil makes sense as a cost-effective option.
However, because krill oil absorbs more efficiently, you may need a smaller dose to get the same benefits. While the upfront cost is higher, it could balance out in the long run, depending on your individual needs and usage.
Winner: Fish oil, for affordability, but krill oil offers value over time.
Krill VS Fish Oil Comparison Table
| Feature | Fish Oil | Krill Oil |
| Source | Derived from fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel). | Extracted from tiny krill (shrimp-like crustaceans). |
| Bioavailability | Triglyceride form (requires more digestion). | Phospholipid form (easier absorption). |
| Antioxidants | Minimal, unless added artificially. | Naturally contains astaxanthin. |
| Taste & Smell | Fishy burps (hello, sushi breath!). | Less fishy due to the phospholipid structure. |
| Environmental Impact | Concerns over overfishing. | More sustainable harvesting practices. |
| Cost | Affordable and widely available. | Premium price but potentially worth it. |
Potential Side Effects and Risks with Safety Tips
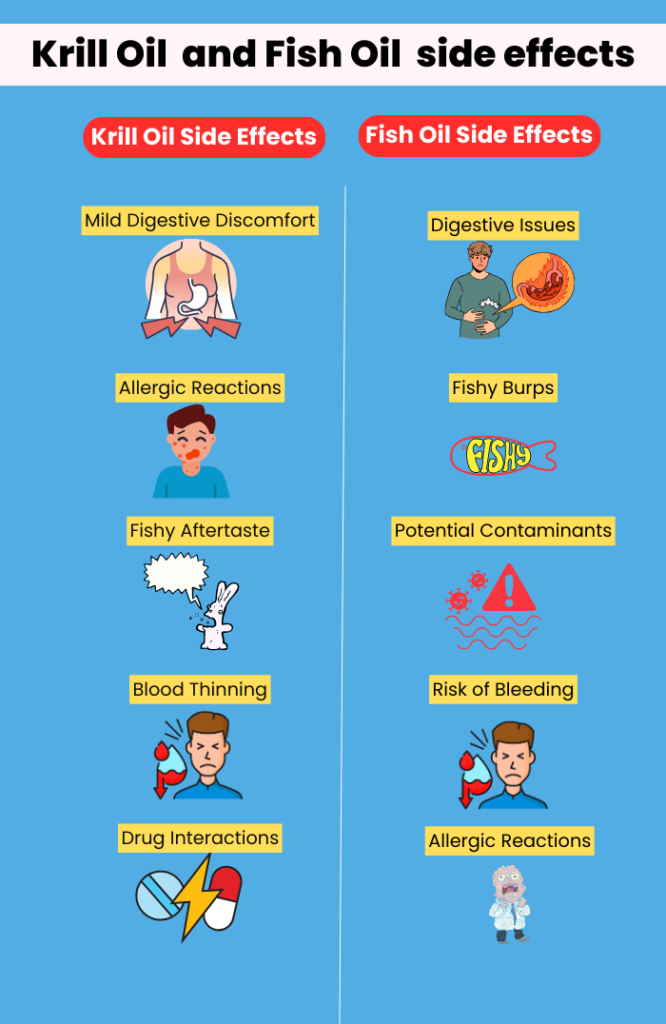
Krill Oil Side Effects
- Mild Digestive Discomfort
Some people experience mild stomach upset, including nausea or bloating, after taking krill oil. Taking it with meals can often prevent this. - Allergic Reactions
Krill oil comes from shellfish, so if you’re allergic to shellfish, it’s better to steer clear. Symptoms like itching, swelling, or trouble breathing could signal an allergic reaction. - Fishy Aftertaste
While less common than with fish oil, some users report a slight fishy aftertaste or burps after taking krill oil. Refrigerating the capsules or taking them with food can help reduce this. - Blood Thinning
Krill oil may thin your blood slightly, which can increase the risk of bleeding, especially if you’re already on blood-thinning medications. This doesn’t mean krill oil is off-limits—it just means a conversation with your doctor is a smart idea. - Drug Interactions
If you’re on medications like aspirin or anticoagulants, krill oil could interact with them. It’s always better to double-check before starting any supplement.
Fish Oil Side Effects
- Digestive Issues
Fish oil can sometimes cause bloating, diarrhea, or an upset stomach. It’s like eating a rich meal your stomach isn’t quite ready for. Taking smaller doses or splitting them throughout the day can help. - Fishy Burps
Fish oil is infamous for leaving a lingering fishy aftertaste or causing “fish burps.” If that’s a deal-breaker for you, enteric-coated capsules or freezing them before consumption can minimize the problem. - Potential Contaminants
Fish oil can contain traces of mercury or other pollutants if sourced from contaminated fish. Reputable brands often test for purity, so it’s worth paying attention to labels when shopping. - Risk of Bleeding
Similar to krill oil, fish oil can thin your blood. If you bruise easily or are on medications like warfarin, you’ll want to consult your doctor first. - Allergic Reactions
Though less common than krill oil, fish oil may still trigger allergies in people sensitive to fish. Symptoms like rashes, swelling, or itching shouldn’t be ignored.
Can I take both krill oil and fish oil together?
While possible, taking both is usually unnecessary since they provide similar Omega-3 benefits. If you’re using krill oil, its superior absorption may make fish oil redundant. Choose one based on your health goals and budget, and consult a healthcare professional to ensure you meet your Omega-3 needs effectively.
Additional Benefits of Krill Oil
- Reduces Inflammation: Omega-3s in krill oil help ease joint pain and stiffness, making it beneficial for conditions like arthritis.
- Improves Cognitive Function: DHA in krill oil supports brain health, aiding memory, focus, and mental clarity.
- Supports Eye Health: Astaxanthin protects eyes from oxidative damage and may reduce digital eye strain.
- Boosts Skin Health: The antioxidant properties of astaxanthin promote healthy, glowing skin by reducing signs of aging.
- Enhances Heart Health: In addition to cholesterol management, krill oil helps lower triglycerides and improve circulation.
Is Fish Oil Still a Viable Option?
Yes, fish oil is a reliable and effective choice for managing cholesterol and improving heart health. It’s widely available, affordable, and proven to lower triglycerides and reduce inflammation.
Fish oil contains omega-3s (DHA and EPA) that support cardiovascular health and may help lower the risk of heart disease. It’s an accessible option for anyone looking to improve their cholesterol levels on a budget. While fish oil doesn’t have the natural antioxidant astaxanthin found in krill oil, high-quality brands often add preservatives to extend shelf life and maintain potency.
If you’ve experienced “fishy burps” or digestive discomfort, opt for enteric-coated capsules or take the supplement with meals to minimize these effects. So, while krill oil may offer some unique benefits, fish oil remains a solid and affordable choice for those seeking heart-friendly omega-3s.
Krill Or Fish Oil? Which One You Should Choose?
Krill oil and fish oil both bring valuable benefits to the table, but your choice depends on what matters most to you:

The best supplement is the one that fits your goals, lifestyle, and budget. If you’re looking for convenience, gentler digestion, and extra antioxidant power, krill oil might be your go-to. But if affordability and accessibility are key, fish oil has you covered.
Now here comes the good part: whichever you choose, you’re taking an important step toward better heart health and cholesterol management. Your health is worth it—start today and make your heart the priority it deserves to be.