Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining good health, supporting everything from heart and brain function to reducing inflammation and promoting eye health. Since many people don’t get enough omega-3s from their diet, supplements have become a popular solution. Traditionally, fish oil has been the go-to source, valued for its high levels of EPA and DHA the two key omega-3 fatty acids.
However, growing concerns about sustainability, dietary choices, and potential contaminants have highlighted algae oil vs. fish oil as a hot topic in the world of supplements, with algae oil emerging as a strong, plant-based alternative.
So, which is better algae oil or fish oil? Both offer unique advantages but differ in their source, environmental impact, nutritional content, and cost. Understanding these differences will help you choose the supplement that fits your health goals, lifestyle, and values.
In this article, we’ll break down these factors and provide a clear guide to algae oil vs fish oil, so you can confidently make an informed decision.
What are algae oil vs fish oil?

Fish oil is extracted mainly from oily cold-water fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. The omega-3 content can differ between wild-caught and farmed fish, with wild varieties typically having more. To make fish oil safe for consumption, it undergoes molecular distillation a process that removes harmful contaminants like mercury and PCBs that accumulate in fish from polluted waters. Fish oil supplements come mainly in two forms: the natural triglyceride form, which is better absorbed, and the ethyl ester form, which is more processed and less bioavailable. A special type, cod liver oil, also provides vitamins A and D but requires careful dosing to avoid toxicity.

Algae oil is sourced from tiny marine algae, the original producers of omega-3s in the ocean’s food chain. It’s produced either in controlled fermentation tanks or through open-pond farming, with tank fermentation offering higher purity. Different algae species, like Nannochloropsis, are cultivated for their EPA and DHA omega-3 content. Algae oil supplements vary too they may contain only DHA or both DHA and EPA and come in oil capsules or powder form, suitable for various preferences and uses such as adding to drinks or cooking.
Key Comparisons: Algae Oil vs. Fish Oil
When choosing an omega-3 supplement, understanding the differences between algae and fish oils is key. Both provide essential fatty acids, but they come from very different sources. Let’s explore how nutrition, sustainability, absorption, and cost compare.
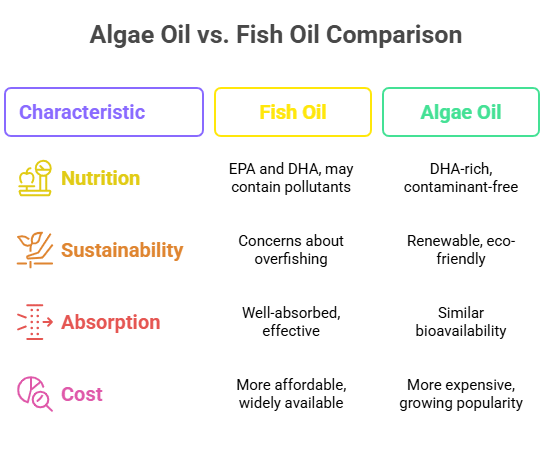
Nutritional Differences
- Fish Oil:
Fish oil naturally contains both EPA and DHA, two essential omega-3 fatty acids that support heart, brain, and eye health. It usually provides a balanced amount of both, making it a strong all-around choice for omega-3 supplementation. However, because fish live in the ocean, fish oil can sometimes contain trace amounts of pollutants like mercury, though purification processes minimize this risk.
- Algae Oil:
Algae oil is often richer in DHA and lower in EPA unless the product is specifically formulated to include both. Since algae are grown in controlled environments, algae oil is free from ocean contaminants like mercury and PCBs, making it a cleaner and purer source of omega-3s. It’s an excellent option, especially for those seeking plant-based supplements.
Sustainability & Environmental Impact
- Fish Oil:
Fish oil production depends on catching large amounts of wild fish, which raises concerns about overfishing and the negative impact on marine ecosystems. This can lead to declining fish populations and harm ocean biodiversity, challenging sustainability with traditional fish oil.
- Algae Oil:
Algae oil is made by farming algae, which grow quickly and don’t require harming wild fish populations. This makes it a renewable, eco-friendly alternative with a much smaller carbon footprint. Algae oil production is more sustainable and helps protect ocean life and the environment.
Absorption & Efficacy
- Fish Oil:
Research shows that omega-3s from fish oil are well absorbed and effectively used by the body. Numerous clinical studies have proven Fish oil to support heart, brain function, and eye health.
- Algae Oil:
Algae oil offers similar bioavailability, meaning the body can absorb and use its omega-3s just as well as those from fish oil. It provides the same health benefits, supporting cardiovascular, cognitive, and visual health, making it a strong plant-based alternative.
Cost & Accessibility
- Fish Oil:
Fish oil supplements are generally more affordable and widely available worldwide. They can be found easily in most health stores and online, making them a convenient option for many people.
- Algae Oil:
Algae oil is typically more expensive because of the specialized farming and production processes involved. However, its popularity is growing fast due to increasing demand for sustainable and vegan-friendly omega-3 sources, which may help lower prices over time.
Who Should Choose Which?
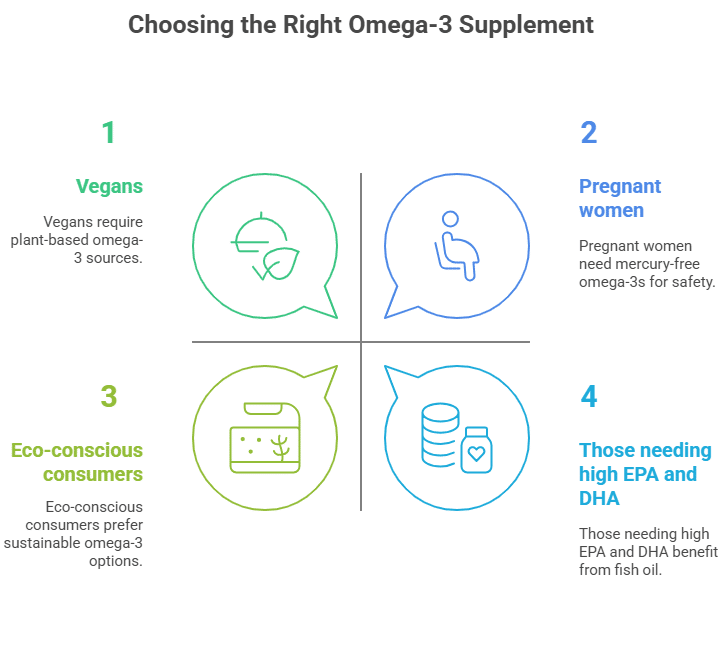
Fish Oil May Be Better For:
- Those needing high EPA and DHA: Fish oil naturally contains both EPA and DHA in substantial amounts, essential for heart health, brain function, and inflammation control. Fish oil might be a better choice if you aim to get a higher combined dose of these omega-3s.
- People without seafood allergies or sustainability concerns: If you have no allergies to fish or concerns about overfishing, fish oil is often more affordable and readily available.
Algae Oil May Be Better For:
- Vegans and Vegetarians: Since algae oil is plant-based, it’s ideal for anyone avoiding animal products but still wanting the benefits of DHA and EPA.
- Pregnant women and sensitive groups: Algae oil is free from mercury and other ocean pollutants, making it a safer option during pregnancy or for those concerned about contaminants.
- Eco-conscious consumers: If protecting marine life and reducing environmental impact is essential to you, algae oil offers a more sustainable and renewable source of omega-3s.
Potential Drawbacks & Considerations
Fish Oil:
- Fish oil can sometimes develop a fishy aftertaste or cause “fish burps,” which some find unpleasant.
- If the oil is not stored correctly, there’s a small risk of oxidation, which reduces effectiveness and can cause rancidity.
- Contamination with mercury or PCBs can occur despite purification processes, so choosing high-quality, tested brands is essential.
Algae Oil:
- Some algae oil products have limited EPA content, focusing mainly on DHA, so you may need to check labels carefully if you want a balanced omega-3 profile.
- Algae oil supplements tend to be more expensive due to more complex farming and production methods, although prices are expected to decrease as demand grows.
Conclusion
When deciding between algae oil and fish oil, factors like nutritional content, environmental impact, cost, and personal values should be considered. Fish oil remains a cost-effective source of both EPA and DHA, ideal for those prioritizing higher omega-3 intake and without issues with seafood or sustainability. Meanwhile, algae oil offers a pure, sustainable, and vegan-friendly alternative, free from ocean contaminants, though it can be pricier and sometimes contains less EPA.
Both supplements deliver comparable health benefits and absorption, making either a valuable addition to your diet. Ultimately, your choice should reflect your health goals, dietary restrictions, and environmental concerns. Whether you choose fish oil, algae oil, or both, ensuring you get enough omega-3s truly matters for long-term wellness.