You’re eating clean, staying active and maybe even tracking your protein but something still feels off. Energy dips, inflammation lingers and recovery takes longer than it should. You’re doing everything right, yet the results don’t match the effort.
This might be where fish oil nutrition comes into play. Our bodies need more than just fuel they require the right kinds of fats to function at their best. Nutrition isn’t only about macros; micronutrients and essential fats are vital in keeping your system balanced. Fish oil might be the missing piece your body has been waiting for.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, aren’t just a passing supplement trend they’re crucial for brain health, joint support, fat metabolism and hormone balance. Without enough omega-3s, your body could be stuck in low gear without you realizing it.
If you’ve been chasing results but still feel off, this article will explain how fish oil can help restore balance from the inside out. You’ll learn what fish oil really does, how it works and how to use it to feel and perform at your best without complicating your routine.
Fish Oil Beyond The Basic?

Fish oil is a concentrated extract of oils derived from the tissues of oily fish like salmon, sardines and mackerel. It is a concentrated source of omega-3 fatty acids, specifically EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). Known as long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, they’re considered essential your body can’t make them on its own, so you have to get them through food or supplements.
But we don’t realize that fish oil isn’t just omega-3s. Depending on the source, it can also contain essential fat-soluble vitamins, trace minerals and antioxidants all of which support your metabolism, immune system and hormonal balance
Our diet tends to be high in omega-6 fats (from processed oils and grains) and low in omega-3s. That imbalance creates chronic inflammation, a significant cause of fatigue, joint pain, fat storage and disease. Restoring that balance with omega-3s from fish oil helps naturally bring your body back into alignment, without overhauling your entire diet.
The Nutritional Profile of Fish Oil: What’s Actually Inside?
When many think of fish oil, they only think of “omega-3s” and that’s fair. But the truth is, fish oil may seem simple, but its nutrient density is powerful. Here’s what you’re really getting in a high-quality fish oil:
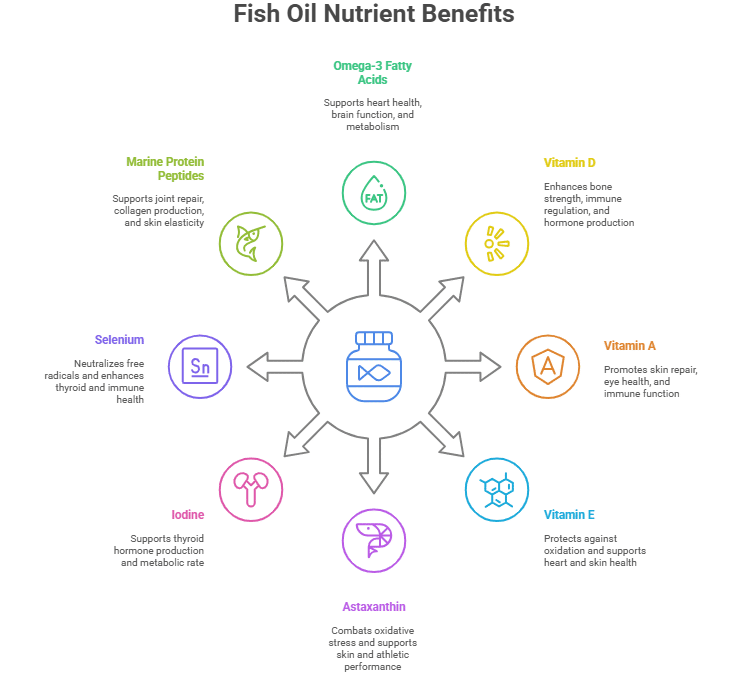
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (EPA and DHA)
At the heart of fish oil’s benefits are the long-chain supplements: EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). These essential fats are responsible for the anti-inflammatory, heart-healthy and brain-boosting effects of fish oil.
- EPA helps reduce chronic inflammation, improve blood flow and support immune function.
- DHA is a structural fat found in brain tissue and the retina. It helps maintain sharp cognition, stable mood and visual performance.
Together, EPA and DHA help regulate metabolism, improve fat oxidation and create a better hormonal environment for muscle building and fat loss.
Vitamin D
Fish oil particularly cod liver oil is one of the few natural dietary sources of vitamin D, a fat-soluble nutrient most people are deficient in.
Vitamin D supports:
- Bone strength and calcium absorption
- Immune regulation
- Hormone production, mainly testosterone and insulin sensitivity
If you’re frequently tired, moody, or struggling to lose fat despite training hard, a vitamin D deficiency could be the hidden cause.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A in fish oil appears in its active form, retinol, making it far more bioavailable than plant-based beta-carotene. This crucial nutrient supports:
- Skin repair and hydration
- Eye health and vision
- Immune function and cellular protection
Athletes, active individuals and those exposed to oxidative stress benefit greatly from consistent intake of bioavailable vitamin A.
Vitamin E
Many high-quality fish oils include vitamin E a fat-soluble antioxidant that protects the delicate omega-3 fatty acids from oxidation. It also supports:
Sustainability & Environmental Impact” section, when discussing alternatives to fish oil
By stabilizing the oil and protecting your body from free radicals, vitamin E enhances the overall effectiveness of fish oil supplementation.
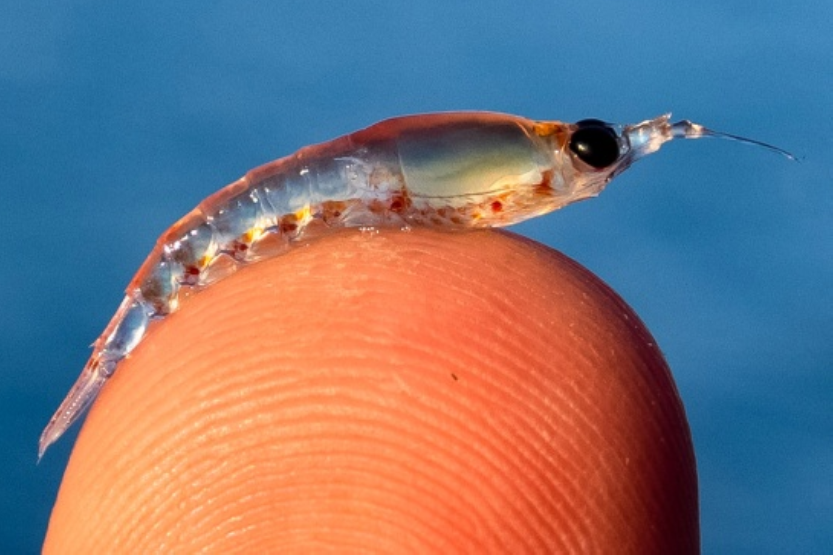
Astaxanthin
What is Antarctic krill used for Krill oil contains a naturally occurring antioxidant called astaxanthin, which gives krill their reddish-pink color. Astaxanthin is known to:
- Combat oxidative stress
- Protect skin from aging and UV damage
- Support athletic recovery and endurance
Its unique antioxidant power complements omega-3s, making krill oil a next-level option for optimizing skin, performance, and cellular longevity.
Iodine
While fish oil isn’t a major source of iodine, it provides small amounts, especially from whole fish or krill.
Iodine supports:
- Thyroid hormone production
- Metabolic rate
- Neurological development
Even in trace amounts, iodine plays a critical role in maintaining balanced energy levels, mood and metabolism.
Selenium
Selenium is a powerful trace mineral found in cold-water fish and some fish oils. It synergizes with omega-3s by neutralizing free radicals and supporting thyroid health. Why it matters:
- Helps convert thyroid hormone T4 to its active form, T3
- Protects the body from oxidative damage
- Enhances immune system resilience
For active individuals or anyone with metabolic concerns, selenium adds another layer of protection and performance to fish oil nutrition.
Marine Protein Peptides
While you won’t find protein in refined fish oil capsules, whole fish and fish-based protein powders offer marine peptides small chains of amino acids with potent bioactivity.
These peptides may:
- Support joint and tendon repair
- Stimulate collagen production
- Improve skin elasticity and hydration
If you’re using fish oil and eating fatty fish regularly, you’re not just getting anti-inflammatory fats you’re also fueling your body with marine-sourced building blocks for recovery and tissue repair.
Key Nutritional Benefits of Fish Oil
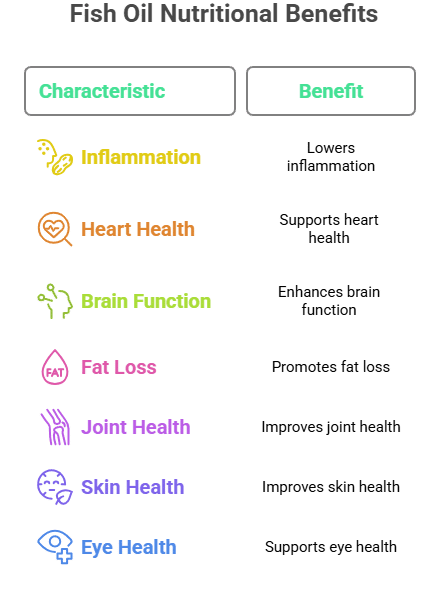
Let’s get into the evidence-backed ways that nutrients in fish oil can change how your body feels and functions.
It Lowers Inflammation The Real Enemy of Progress
Most people think inflammation only shows up as swelling or injury but chronic low-grade inflammation is a silent killer. It keeps you tired, sore and inflamed even when doing everything else right.
Omega-3s in fish oil act like a fire extinguisher for inflammation. They help downregulate pro-inflammatory pathways and promote healing, whether it’s sore joints, slow recovery or an immune system always on edge.
It Supports Heart Health Without Prescription Drugs
Fish oil has been shown to reduce triglyceride levels, lower blood pressure, improve HDL (good cholesterol) and reduce the risk of arterial plaque buildup.
This isn’t just for people with heart problems it matters even more if you’re active. The heart powers everything from endurance to lifting capacity to hormone transport. Keep it strong and everything else will run smoother.
It Enhances Brain Function, Focus and Mood Stability
Your brain is nearly 60% fat a massive portion of that is DHA. If you’re not getting enough DHA, you may feel foggy, forgetful or emotionally unstable. Fish oil helps nourish your brain, improving mental clarity, concentration and emotional resilience.
Research has also linked omega-3s to lower rates of anxiety, depression and cognitive decline.
It Promotes Fat Loss
Fish oil doesn’t burn fat directly like a thermogenic but it helps your body become more efficient at burning fat. Studies show omega-3s can:
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Increase fat oxidation during exercise
- Support hormonal balance (including cortisol and leptin)
The result? Your metabolism runs more efficiently, your body stores less fat, and your recovery boosts.
It Improves Joint Health and Muscle Recovery
EPA and DHA can reduce joint stiffness, soreness and pain, making staying consistent with your workouts easier. Omega-3s also reduce muscle damage and soreness after training, speeding up repair and helping you bounce back stronger.
It May Help Skin Look and Feel Better
Dry, flaky skin? Breakouts? That might be a sign of low omega-3 levels. Fish oil supports the skin barrier and helps regulate oil production. It may reduce acne and soothe skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis. Over time, skin can appear less irritated and more hydrated.
It Supports Eye Health and Vision
DHA is highly concentrated in the retina. When levels are low, vision can suffer. Fish oil may help reduce dry eye symptoms and lower the risk of age-related macular degeneration. If your eyes feel strained or tired, especially from screens, this could help.
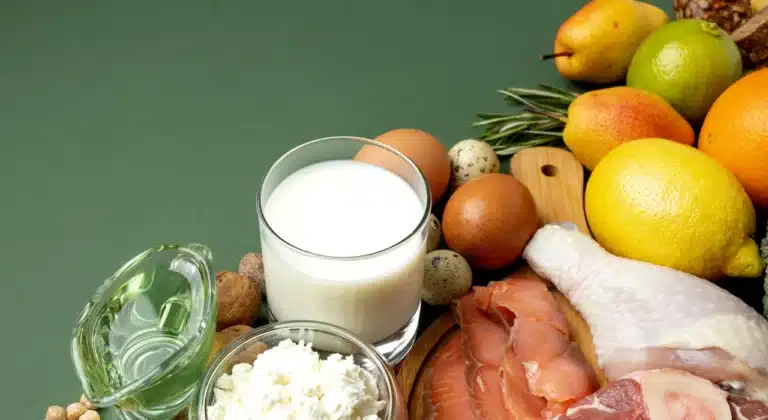
The Best Sources of Fish Oil: Food First, Then Supplements
If you can get your omega-3s from food, do it. Whole foods provide additional nutrients like protein, selenium, iodine, and vitamin D.
- Wild salmon
- Sardines
- Mackerel
- Anchovies
- Trout
- Krill
- Cod liver oil
How to Incorporate Fish Oil for Maximum Impact
It’s not just what you take that matters it’s how and when you take it that determines the real-world results. Fish oil is full of nutrients but like any, it works best when used consistently and strategically.

Here’s how to make fish oil a part of your routine in a way that’s simple, sustainable, and effective.
Take Fish Oil With Meals That Contain Fat
Omega-3 fatty acids are fat-soluble, which means they are best when taken with dietary fat. This doesn’t mean you need to take fish oil with a high-fat meal but pairing it with a few eggs, some avocado or a handful of nuts can improve absorption significantly.
Best practice: Take your fish oil with breakfast or dinner, mainly if the meal includes healthy fats.
Split Your Dose (Morning and Evening)
Instead of taking a large amount all at once, split your fish oil dose into two smaller servings one in the morning and one at night. This keeps your omega-3 levels more stable throughout the day and may improve your body’s ability to utilize it for things like inflammation control and cognitive function. Like
- Morning: 1,000mg with eggs or oatmeal and nuts
- Evening: 1,000mg with dinner (fish, greens, olive oil)
This also reduces the chance of any unpleasant fishy aftertaste or reflux.
Post-Workout Recovery Booster
If your goal is better recovery, less soreness and faster performance gains, consider taking one of your doses post-workout, especially after intense strength or endurance sessions.
Omega-3s have been shown to:
- Decrease muscle inflammation.
- Support joint resilience.
- Improve protein synthesis when combined with a high-protein meal.
Pro tip: Pair your post-workout protein shake with a small meal that includes healthy fats and your fish oil supplement.
Be Consistent Even on Rest Days
One of the most common mistakes? People skip fish oil on non-training days.
Fish oil isn’t a pre-workout or recovery shake it’s a foundational nutrient. For maximum benefit, your body needs a steady supply of omega-3s daily, not just when you train.
Consistency is key. Treat fish oil like brushing your teeth it’s something you do every day, no matter what’s on the schedule.
Start With the Right Dose
The general recommendation is 1,000 to 3,000mg of combined EPA and DHA per day. But this depends on your diet, activity level and specific health goals.
- For general health and prevention: ~1,000mg/day
- For joint pain, inflammation, or fat loss support: ~2,000–3,000mg/day
- For therapeutic or clinical needs: Talk to your healthcare provider
Make sure to read the label carefully. Some supplements advertise “1,200mg of fish oil” but only include 300mg of EPA/DHA, which won’t cut it for real impact.
Choose a Form That Fits Your Lifestyle
There’s no one-size-fits-all. What matters most is that you’ll actually take it consistently.
- Capsules: Convenient and mess-free. Choose enteric-coated if you’re prone to fishy burps.
- Liquid fish oil: Great for larger doses. Some come flavored (lemon, orange) and mix well into smoothies.
- Krill oil: Naturally contains astaxanthin and may be easier to absorb, though usually more expensive.
- Cod liver oil: Delivers EPA, DHA, plus natural vitamins A and D ideal if you want a full-spectrum nutrient boost.
Pick the format you’ll stick with and remember: quality trumps quantity.
Track Your Energy, Inflammation, and Focus
The best way to know if it’s working? Pay attention to how you feel. After 2–3 weeks of consistent use, you might notice:
- Less joint stiffness in the morning
- More mental clarity throughout the day
- Fewer energy crashes or mood swings
- Smoother recovery between workouts
These are real markers of systemic change and signs that your omega-3s are doing their job. Keep a short weekly journal. Track energy levels, joint soreness, mental clarity and sleep quality.
Potential Considerations and Side Effects
While fish oil is generally safe, some factors should be considered:
- High doses may lead to blood thinning, increasing bleeding risk.
- Possible side effects: Fishy aftertaste, indigestion or diarrhea.
- Mercury concerns: Choose high-quality, purified fish oil supplements to avoid contaminants.
- Interactions: May interact with blood thinners (e.g., warfarin) or blood pressure medications.
Final Thoughts: Is Fish Oil Worth Adding to Your Routine?
In a word? Yes. Fish oil is one of the few supplements that delivers real, measurable benefits across multiple systems brain, heart, joints, fat metabolism, mood, and recovery. If you’re training hard, eating clean, and still feeling like something’s missing, omega-3s could be that missing link.
This isn’t about trends or hype. It’s about giving your body what it actually needs to perform, heal, and thrive.
So, the next time you build your supplement stack or plan your meals, ask yourself: Am I fueling my body with what it needs to recover, focus, and grow?
Fish oil may not be flashy, but it’s full of nutrients your body needs most. And sometimes, that’s precisely what you need.








