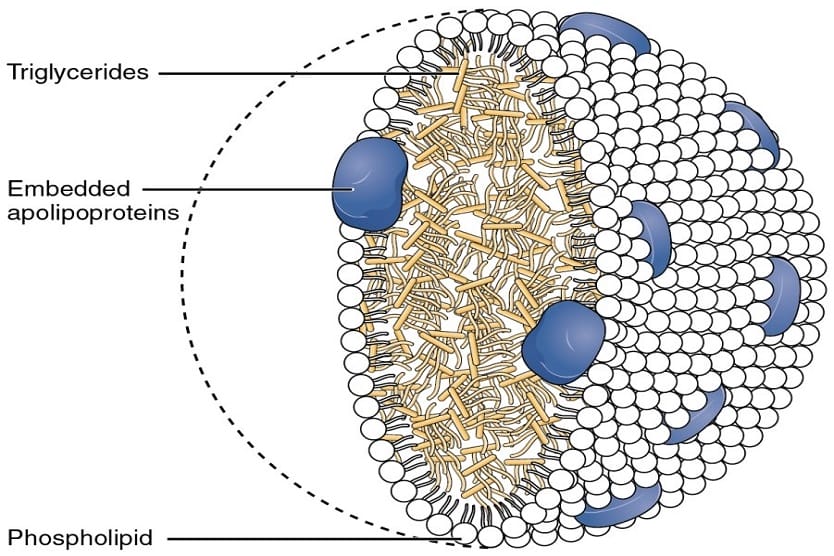
When it comes to understanding fats, particularly in supplements like krill oil, knowing the difference between triglycerides and phospholipids is essential. Both types of fats play crucial roles in the body, but they function in distinct ways. Triglycerides, commonly found in dietary fats, are primarily used for energy storage, while phospholipids are key components of cell membranes and are more easily absorbed by the body.
This distinction is particularly important when comparing omega-3 triglycerides vs phospholipids. Omega-3s in triglyceride form, such as those in fish oil, require more digestive processing. On the other hand, phospholipid-bound omega-3s, like those found in krill oil, offer better bioavailability, allowing the body to absorb and utilize them more efficiently.
In this guide, we’ll explore the difference between triglycerides and phospholipids, explain their roles in health, and discuss why krill oil is a superior source of omega-3s due to its phospholipid content. Understanding these distinctions can help you make informed decisions about which omega-3 form is best for your health.
[ez-toc]
What Are Triglycerides?
Triglycerides are a type of fat made up of three fatty acids attached to a glycerol backbone. Think of them as little energy packs stored in your body for when you need fuel. When you eat, your body converts any excess calories into triglycerides, which are then stored in fat cells. When energy is required, these fats are released and burned to keep you going. This process makes triglycerides one of the body’s primary sources of energy.
You’ll find triglycerides in most of the fats you eat, like butter, oils, and fatty foods. They’re also present in common omega-3 supplements, such as fish oil. In this form, triglycerides carry omega-3 fatty acids, but the body has to break them down and reassemble them for use, which takes longer compared to other forms like phospholipids.
While triglycerides are important for energy, high levels in the blood can pose a health risk. Elevated triglycerides are linked to heart disease and other cardiovascular issues, making it essential to maintain a healthy balance. This is where understanding the difference between triglycerides and phospholipids becomes crucial, especially when considering omega-3 supplements like krill oil, which are more efficiently absorbed due to their phospholipid structure.
In short, triglycerides play an essential role in energy storage, but balancing their levels is key to long-term health.
What Are Phospholipids?
Phospholipids are essential fat molecules that make up the very structure of our cells. They’re composed of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group. Picture them as the building blocks of cell membranes, creating protective barriers around every cell in your body. Without phospholipids, your cells wouldn’t be able to function properly or communicate with one another.
One of the standout features of phospholipids is their role in carrying omega-3s in a more efficient form. Phospholipid-bound omega-3s, like those found in krill oil, are more bioavailable—meaning they’re absorbed and used by the body more quickly and effectively than omega-3s in triglyceride form. This means you get the benefits faster, without your body needing to break them down as much.
You’ll find phospholipids in sources like krill oil, certain plants, and marine organisms. When it comes to health, phospholipids are champions. Their structure allows for easier digestion and absorption, which contributes to better brain function and cardiovascular health. They help your cells stay strong, ensuring vital processes keep running smoothly.
In short, when comparing phospholipids vs triglycerides, phospholipids take the edge for their superior absorption and overall health benefits. Whether it’s boosting brain power or supporting heart health, phospholipid-bound omega-3s, like those in krill oil, offer a more efficient way to get the nutrients your body needs.
Key Differences Between Triglycerides and Phospholipids
When it comes to fats, it’s easy to lump them all together. But the difference between triglycerides and phospholipids is like comparing apples to oranges—they have distinct roles and benefits. Let’s break down the key differences in a way that’s easy to understand and helps you make better choices for your health.
1. Structure:
Imagine triglycerides as a simple three-legged stool. They consist of three fatty acids attached to a glycerol backbone, and their primary job is energy storage. On the flip side, phospholipids are like a two-legged stool with a little twist—a phosphate group. They have two fatty acids attached to glycerol, plus a phosphate group that makes them ideal for building cell membranes. This makes phospholipids more like construction workers for your body, while triglycerides are the fuel tanks.
2. Function:
Triglycerides are the body’s energy reserves. When you consume more calories than you burn, they’re stored as fat, and your body taps into them when it needs energy. Phospholipids, on the other hand, are the architects of your cells. They form the walls of each cell, keeping everything organized and functional. Without phospholipids, your cells wouldn’t be able to hold together.
3. Bioavailability:
This is where things get interesting. Omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart and brain health, come in both triglyceride and phospholipid forms. Here’s the catch: phospholipid-bound omega-3s, like those found in krill oil, are much more bioavailable. That means they’re absorbed and used by the body faster and more efficiently compared to omega-3s in triglyceride form, like those in most fish oils. It’s like choosing between fast-track delivery and standard shipping—phospholipids get the job done quicker.
4. Health Benefits:
Because of their better absorption, phospholipid-bound omega-3s deliver benefits faster and more effectively. They support brain health, protect your heart, and even help with inflammation. Triglycerides still have their place, providing necessary energy, but when you’re aiming for health-boosting nutrients like omega-3s, phospholipids win hands down.
5. Sources:
Triglycerides are common in most dietary fats—think butter, oils, and fatty foods. Phospholipids, on the other hand, are found in foods like eggs, soy, and krill. While both are necessary, krill’s phospholipid-bound omega-3s make it a more efficient source for those seeking to improve heart and brain function.
In a nutshell, phospholipids are more than just fats—they’re the foundation of your cells and offer better nutrient absorption. Triglycerides are essential for energy storage but don’t deliver omega-3s as efficiently. When comparing omega 3 triglycerides vs phospholipids, it’s clear that phospholipids, particularly in krill oil, bring added benefits for anyone looking to support their long-term health.
Krill: A Superior Source of Omega-3 Phospholipids
When it comes to omega-3, krill stands out as a powerful, highly effective option. What sets krill apart is that its omega-3s are bound to phospholipids, making them more easily absorbed by the body. Unlike fish oil, which contains omega-3s in triglyceride form, krill oil offers faster absorption and better utilization of these essential fats.
Why does this matter?
Imagine trying to send a package through two different delivery systems. Fish oil, with its triglyceride-bound omega-3s, is like the regular postal service—it gets the job done, but it’s slower. Krill, on the other hand, is like express shipping, thanks to its phospholipids. Your body recognizes and absorbs these omega-3s much faster, delivering quicker health benefits like improved heart and brain function.
Beyond just omega-3s, krill has an added bonus: astaxanthin. This powerful antioxidant not only protects your cells from damage but also gives krill oil its rich red color. Astaxanthin helps reduce inflammation, supports skin health, and even boosts the immune system—making krill oil a more comprehensive supplement than fish oil.
When it comes to cholesterol, krill oil and triglycerides play a key role. Research suggests that krill oil, with its phospholipid-bound omega-3s, may be more effective at balancing healthy cholesterol levels compared to fish oil. This makes it a great choice for supporting cardiovascular health. The phospholipids in krill oil not only help lower “bad” LDL cholesterol but also raise “good” HDL cholesterol, promoting better heart health overall.
So, when comparing omega-3 triglycerides vs phospholipids, krill oil comes out on top. Its superior absorption, combined with the powerful antioxidant benefits of astaxanthin, makes it an excellent choice for anyone looking to maximize the health benefits of omega-3s. Whether you’re aiming to boost brain function, support heart health, or maintain healthy cholesterol levels, krill oil provides a faster and more effective way to meet those goals.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Omega-3 Form for Optimal Health:
Understanding the difference between triglycerides and phospholipids is key when it comes to choosing the right omega-3 supplement. Triglycerides, found in traditional fish oil, are effective but require more processing by the body before they can be fully absorbed. In contrast, phospholipid-bound omega-3s, like those in krill oil, are more bioavailable, meaning they’re absorbed faster and more efficiently, allowing your body to reap the benefits sooner.
For anyone looking to optimize their health, krill oil is a standout choice. Its superior absorption, combined with the powerful antioxidant astaxanthin, makes it a premium source of omega-3s. Whether your goal is to support heart health, boost brain function, or reduce inflammation, krill oil offers a more effective way to get the nutrients your body needs.
Ultimately, the right omega-3 supplement depends on your specific health goals. If you’re seeking a solution that delivers maximum benefits quickly and efficiently, krill oil, with its phospholipid-bound omega-3s, is a smart choice to help you achieve those goals.